Game theory is the study of how people behave in strategic situations.
If you know what your competitor will do, you can continue doing what you are doing. However, when you don't know others' strategies, your action depends on how others might respond to that action. That's a strategic decision.
| Approach | |
|---|
| Basic Economics | When you make decisions based on factors relevant to only you. |
| Game Theory | To make strategic decisions, you need to factor in external agents' actions, such as your competitors' pricing strategy, which will impact your product prices. |
There are 5 common games:
- Prisoner's Dilemma
- Stag and Hare
- Hawk and Dove
- Battle of the Sexes
- Chicken
In all games, the system eventually settles at Nash Equilibrium, a stable combination of strategies.
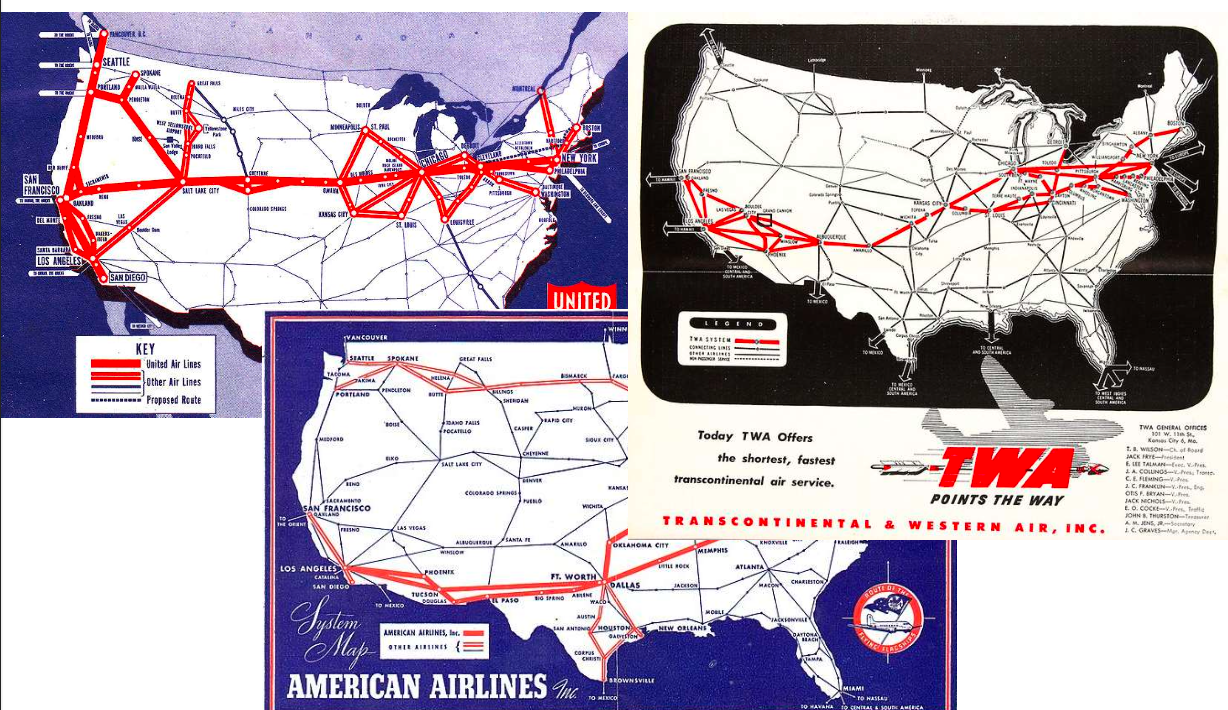
Game Type 1 - Prisoner's Dilemma
- Applications - When multiple parties share common resources e.g. Oil Well.
- Outcome - Two individuals might not cooperate, even if it is in their best interest to do so.
- Dilemma - The conflict between individual rationality and collective rationality. Each prisoner is tempted to betray the other to minimize their own sentence, but if both prisoners betray, they both end up with a worse outcome than if they had both cooperated. Best collective outcome is achieved by cooperation. However, individuals are incentivized to defect. Because of trust issues, a suboptimal outcome is likely in such situations.
- Strategy - If there are finite number of plays, then pick your dominant strategy. However, if there are infinite number of plays, then cooperate with your competitor. ⚠️ To prevent companies from cooperating, we have anti-trust laws.
PD Example 1 - Iran vs Iraq Oil Production Dilemma
Both countries produce oil, but if both produce a lot of oil, oil prices go down.
| Iran ⬇️ Iraq ➡️ | High Production (dominant) | Low Production |
|---|
| High Production (dominant) | 1. Both get $40 billion | 2. Iraq (30 bn), Iran (60 bn) |
| Low Production | 3. Iraq (60 bn), Iran (30 bn) | 4. Both get $50 billion |
- There is one equilibrium, both parties choose their dominant strategy.
- #4 is good for society because more wealth ($100 bn.) is created
- For countries, it makes sense to take #1 (dominant strategy) because you can't trust competitor. Thus,
PD Other Examples - Anywhere There is Common Resource
-
As a land owner, you get ownership of land till core. As Oil companies own oil wells, it makes sense to over-invest and produce as much oil as possible. If you don't, then your competitor will over-invest and take your oil share, as you can't stop them from pumping your oil.
-
When you go out with your friends and split the check, Order more as your friends will likely do so, and you will pay their share.
-
Biologist approach. Imagine the world is a mix of Cooperators and Defectors. In equilibrium, there will be no cooperators because, in multiple rounds, there will be one defector, and going forward, cooperators will switch to defectors as well.
If there are a finite number of plays, then there is no benefit to being a cooperator.
However, if there is an unlimited number of plays, then there is a benefit to being a cooperator. For example, Amex won't give you a credit card if you come with a fixed lifeline.
-
McDonald's doesn't hire employees from the neighborhood where their store is located because that increases the risk of free food. Cooperation emerges when you run into similar people every day. The solution is to rotate troops so that people can avoid establishing relationships.
-
When brushing your teeth, you rearrange bacteria in your mouth, ensuring that bacteria don't build relationships and establish a company.
Practical Resolution - Build Trust, Mergers, Gov Regulations
When you can't trust your competitor but both parties want to cooperate, you establish a trust so that if anyone breaks the trust, there will be a penalty. For example, Texas and Oklahoma have union trust. California doesn't have this law because California's oil is different - it is more solid, unlike Texas's liquid oil. You can only suck your oil, so you don't need such trust.
| Different Market Types | No. of firms | Product Types |
|---|
| Monopoly | One | Utility - Tap water, Sewer |
| Oligopoly | Few | Crude Oil |
| Monopolistic Competition | Many | Differentiated products - Movies, Novels, Pen, Laptop |
| Perfect Competition | Many | Identical products - Wheat, Milk |
Questions
- Why don't two countries sign a contract?
- Companies can't sign a contract because that would be against anti-trust laws.
- Countries can't sign a contract because the law can't be enforced across borders.
Game Type 2 - Stag and Hare
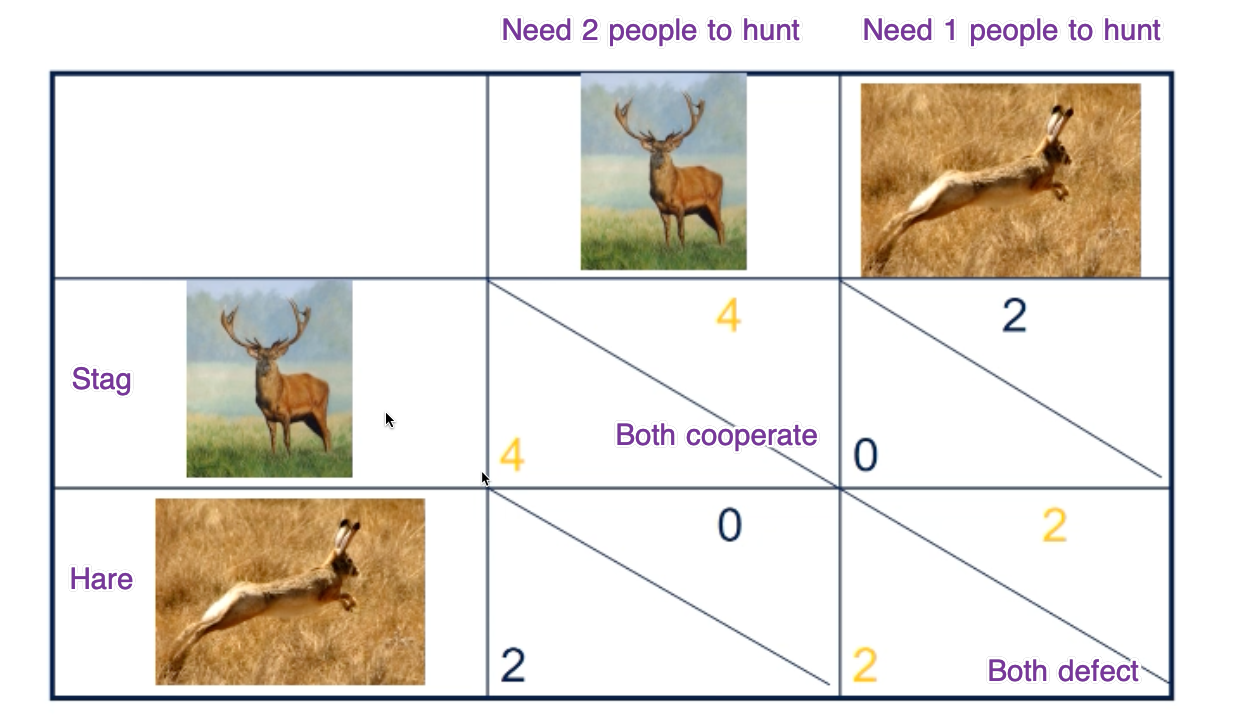
Two hunters (players) must decide whether to hunt for a stag (a large and valuable animal) or a hare (a smaller and less valuable animal). Successfully hunting a stag requires cooperation between the two hunters. However, hunting a hare can be done individually and is a safer, though less rewarding, option.
| Options | |
|---|
| Individual perspective | Hunt Hare, safe choice, guarantees a moderate payoff regardless of the other player's choice. |
| Collective perspective | Coordinate to hunt stag, safe choice, but there is a risk of one player defecting and choosing to Hunt Hare instead. |
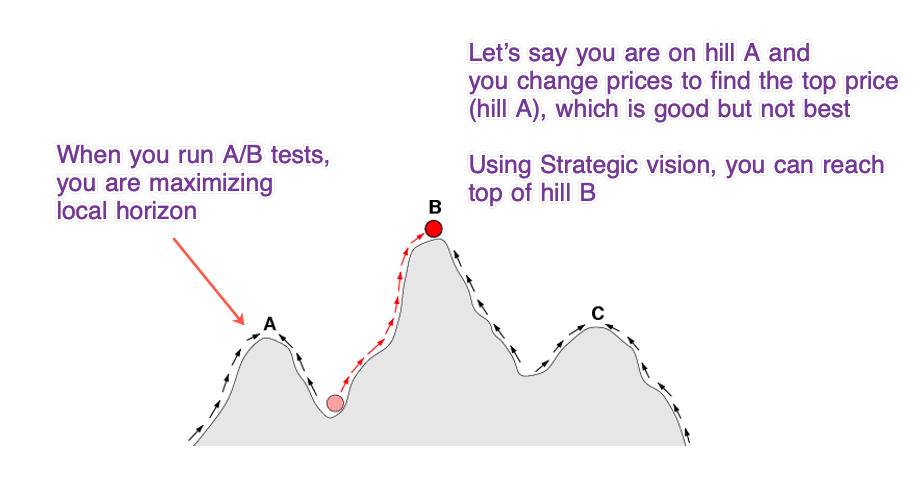
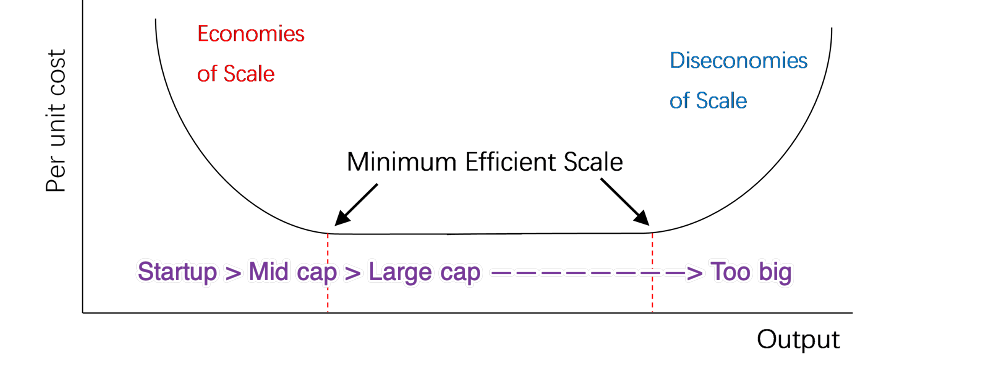
In this there are two equilibriums - Stag + Stag (better), Hare + Hare, but one is better than other. In such examples, whatever the world starts with becomes norm. Thus, if the world has 51% hunters (stag + stag) then eventually equilibrium will reach at all hunters 100% (stag + stag). In business it's called First Movers.
There is advantage if you are a first mover as you can set your own rules and world will follow because of network effects. When intel established their open standard everyone followed their suit, leaving rest of the competitor bankrupt.
- Positive feedback loop - Rich gets richer, Poor gets poorer.
- Network effects - D-Box chair and movie theatres.
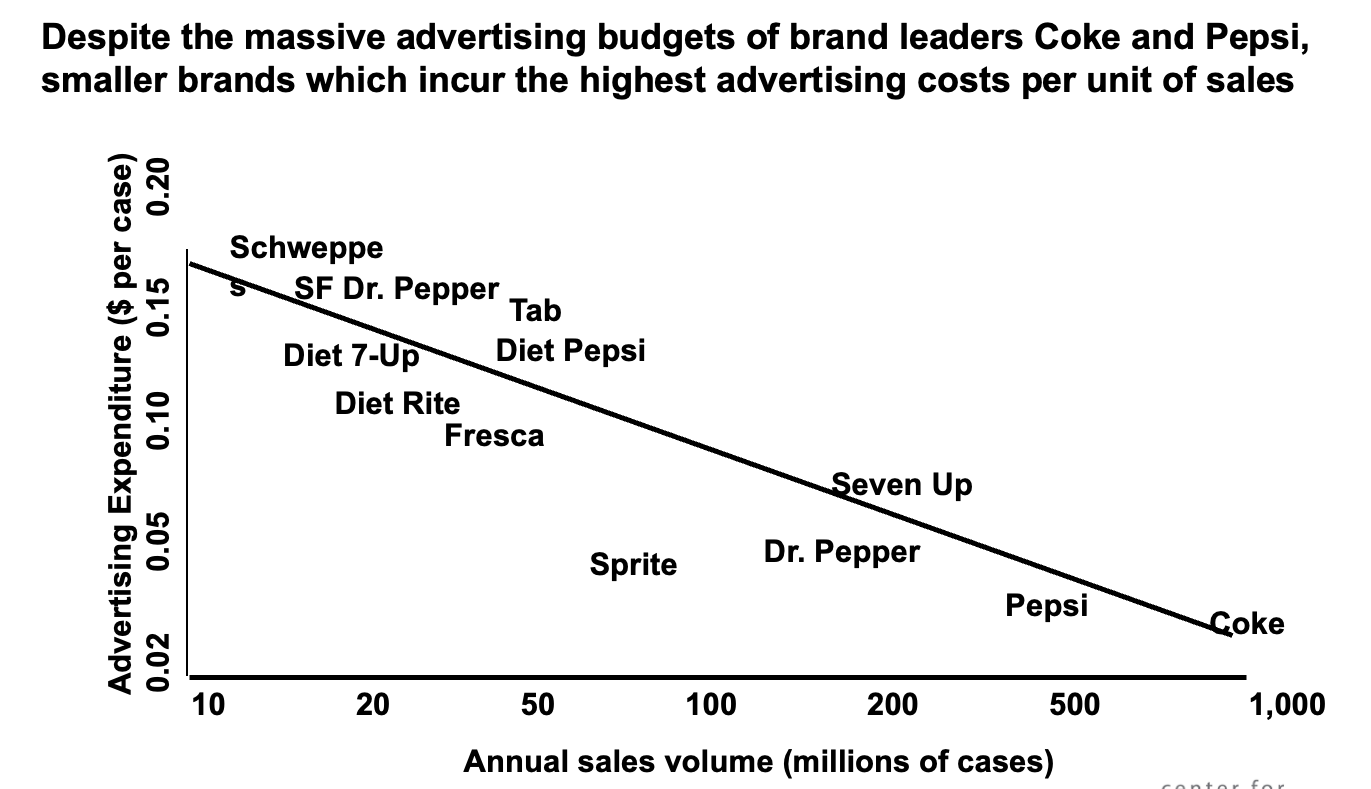
Case 1 Ready-to-eat (RTE) Breakfast Cereal
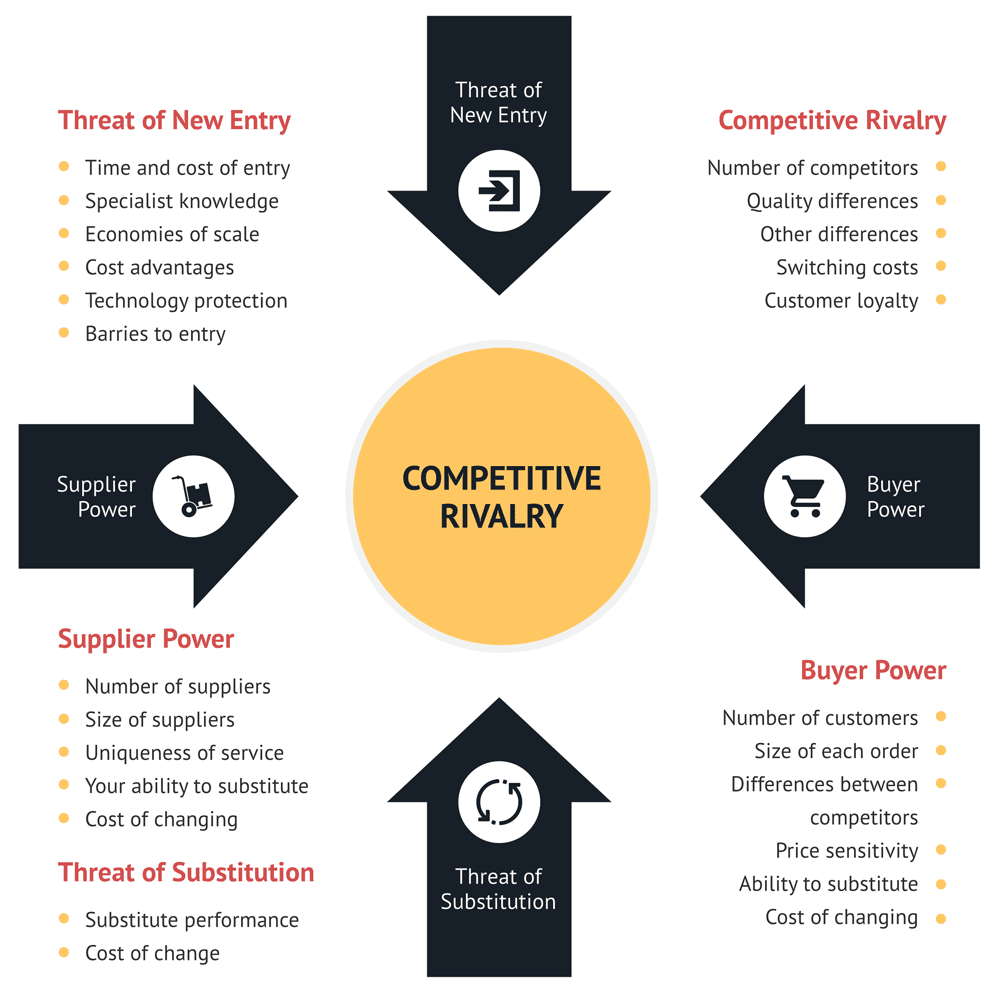
In 1993, Cereal industry was highly profitable. To analyze an industry, start from porter's five forces framework to understand why it is highly profitable. Whenever you have two big players in the market, there are two main risks.
| Risks | Why? |
|---|
| Barriers to Entry | New Entrants have to pay significant money for shelf space, sales staff, R&D, and marketing. Moreover, it was for one brand and each company has around ~15 brands. |
| Rivalry Among Competitors | In Cereal case, there was no rivalry among key players, enabling them not to steal from each other customers. They didn't go into price wars. |
| Bargaining Power of Buyers | Not applicable |
| Bargaining Power of Suppliers | Not applicable |
| Substitutes and Complements | Not applicable |
Assorted Concepts
| Concept | Details |
|---|
| Concentrated Industry | Highly concentrated industry doesn't necessarily mean highly profitable. Quite the opposite, the intense competition can wipe off all profits. For example, Uber and Lyft are highly concentrated, but they don't make any money. Companies have to figure out how not to steal from each other customers. |
| Trade promotions are bad | They don't increase sales. They only transfer your profit to retailers. It leads to a bidding war. Target is telling Kellogs to give me $3 million to place your cereals at a premium location. Target will tell GM to bid $4 million for premium space. How do we stop trade promotions? This can only be done when all competitors get into an agreement not to pay for the bid. When this strategy was executed, Quaker Oats were free riders, and their market share jumped. |
| Coupons are good | They are for price-sensitive customers and increase sales. |
The margins of the big three cereal makers are shrinking because of private labels. There is pressure to increase profitability. Kellogs and General Mills are not competing on prices but promotions/advertisement.
Operating Income = Revenue ⬇️ - COGS - SGA (includes marketing) ⬆️
A decrease in prices or an increase in marketing expenses has the same practical effect. If a company is increasing its marketing expense, then its competitor has to also increase their marketing expense.
How Competitors are Attempting to Kill Private Label Cereals
For competitors to kill private labels, they need to find the weakest link in the value chain and kill that.
- Customer | ✅
- Retailers | ✅
- Wholesalers | ✅
- Distributers | ✅
- Manufacturers | ✅
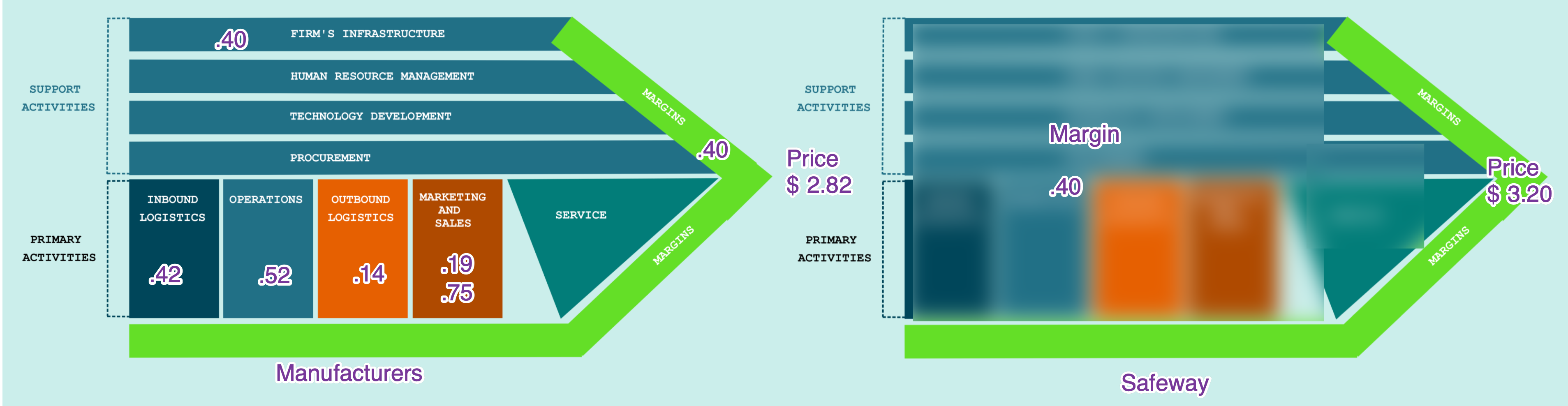
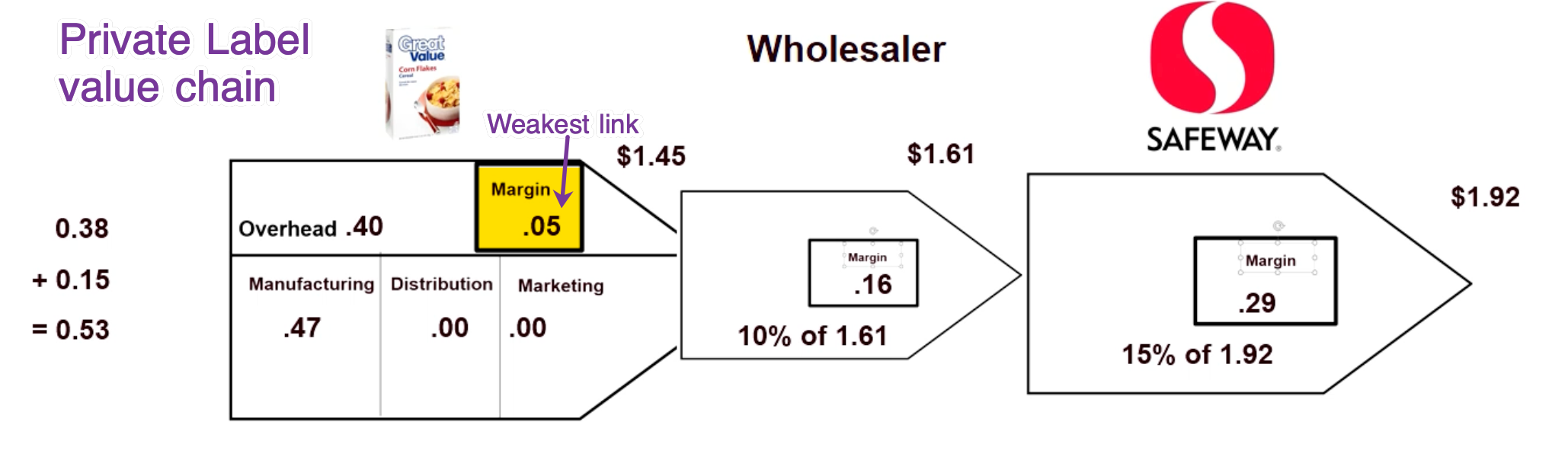
Targeted Retaliation: Weakest link in the private label value chain is manufacturers, as their margin is only $0.05 per box. So big companies started to cut down prices a bit, which pushed down prices of private label cereals, cutting down manufacturers. Moreover, big cereal makers only cut prices on brands that are imitated by private labels.
| Big Players Actions | | |
|---|
| 1. Price Reduction | Put pressure on private label manufacturers | 🔻 $.12/lb |
| 2. No Trade Promotions | No bidding to retailers for shelf space. | 🔺 $.14/lb |
It's is an example of a prisoner's dilemma. What if General Mills implements this and Kellogg's doesn't? Kellogg's will take most of the profit. Thus, if one company decide to do it, they will hold a press conference and soon enough the competitor will do the same actions. Since it's a long term game, it makes sense for companies to cooperate, instead of defecting.
As big players stopped paying money to Safeway for shelf space and private label manufacturers margin dwindling, Safeway started approching small brands such as Post, Quaker oats for shelf space bidding. Consequently, there market share increased. These are called Free Riders.
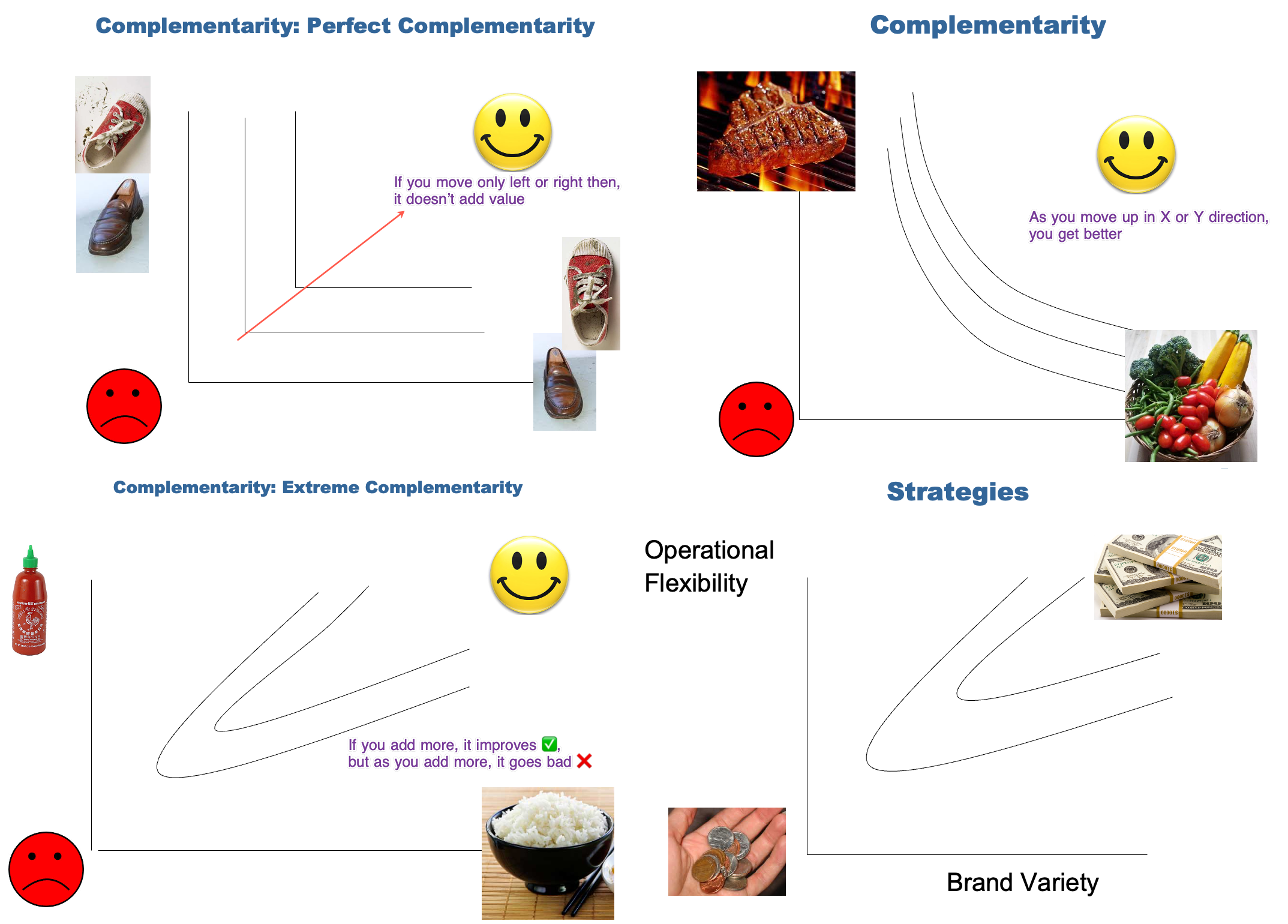
Concept Value Net Model - FRENEMY (Friend + Enemy)
Cooperation and competition between organizations are not only desirable but also necessary when doing business.
Customers | Competitors | Suppliers | Complementors
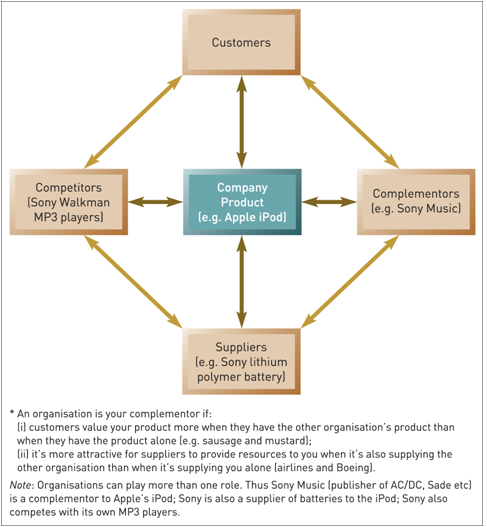
All of these entities are not your enemies but FRENEMY. Apple and Samsung, you and your spouse; and you and your housemates.
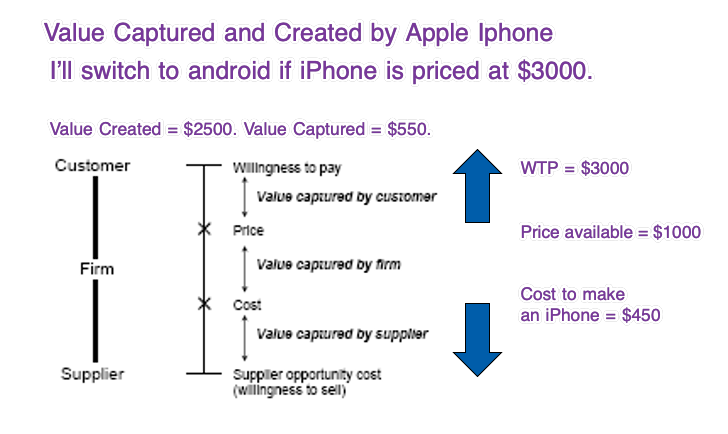
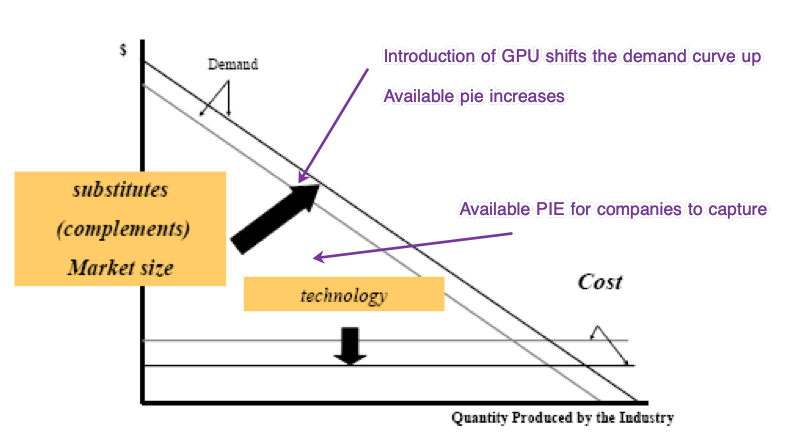
- Value Creation: Value is created by establishing a standand. Once it's established, then you are locked in, and you don't need to worry about takeoff. Open Source Standards increase the size of the pie. For example, speaking same language increases value. Most standards emerge bottom-up, not top-down.
-
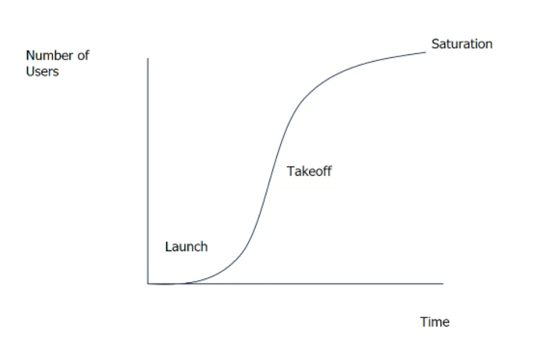
-
Adoption dynamics of a new product: Launch ➡️ Takeoff ➡️ Saturation.
-
Typewriters - why do we have a querty keyboard? It was not designed to be fast or have fewer errors, but because they didn't jam. Now, we no longer have this limitation, but we are locked in with this standard. We can't ship to new standards because who is going to create hardware and software for the new standard?
| Value appropriation | Market Acceptance |
|---|
| Definition | Ability of a company to capture and retain a portion of the value it creates. | Degree to which a new product or service is embraced by the market. |
| How | Competitive advantage, pricing strategy, intellectual property rights, negotiation power | Product-market fit, customer needs, marketing effectiveness, timing. |
| Example ✅ | Apple because of innovation, brand loyalty, premium pricing strategy | Tesla cars because of timely introduction of technology in line with growing environmental concerns |
| Example ❌ | Kodak invented the core technology in digital camera but failed to capitalize on this innovation effectively. | Google glass because of privacy issues, lack of practical use cases, and high cost. |
Case 2 Intel vs IBM - Value Capture Strategy
Intel History
| Intel | Toshiba/NEC |
|---|
| R&D | Great at innovations | Outsourced to Intel or copied patents from Intel |
| Manufacturing | | Great at manufacturing |
- Intel is good at R&D, but they can't copyright their RAM drives, so they can't make money. They were in patent pooling industry.
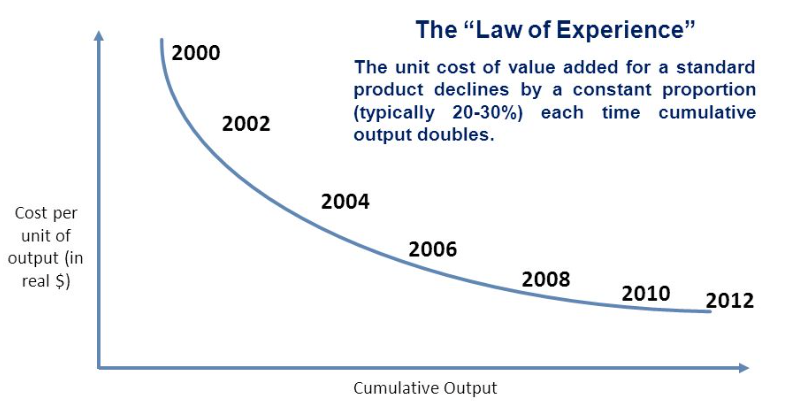
- Intel introduced new designs frequently, and there were 6-9 months of delay when competitors introduced new designs. Intel had this time window to recoup its R&D cost. After nine months, competitors introduced cheaper rams by copying Intel's design. The only option Intel had was to introduce a new design. As time went by, Japanese companies got smarter, and the time to copy was reduced.
- They finally withdrew from the RAM business and planned to create a new business where they could have intellectual property.
- Similar thing is happening with fast fashion industry these days such as H&M.
Case Background
- Intel's Innovation: developed the 8088 microprocessor in 1970s, making it more affordable to implement in PCs.
- IBM's Entry into PCs: IBM decided to enter the burgeoning personal computer (PC) market. They needed a reliable processor for their IBM PC and chose Intel.
Value Capture Dynamics
Intel's Position:
- Innovator and sole supplier of 8088: Strong position. The success of the IBM PC meant a high demand for the 8088, directly benefiting Intel.
- Brand Recognition: Intel's association with IBM, a leader in computing, boosted Intel's brand recognition.
IBM's Strategy:
- Open Architecture: IBM's PC was designed with an open architecture, meaning that other companies could produce compatible hardware. While this strategy helped IBM quickly capture market share, it also allowed other companies to produce IBM-compatible PCs.
- Focus on Market Penetration: IBM's primary goal was to dominate the PC market. They were less concerned with controlling the entire value chain (like microprocessor manufacturing) and more focused on establishing the IBM PC as a standard.
Outcome and Implications
- Intel's Success: Intel successfully captured significant value from its 8088 microprocessor. IBM's PCs and IBM-compatible PCs drove large-scale production and sales for Intel.
- IBM's Mixed Results: While IBM did succeed in making the IBM PC a market standard, their open architecture approach eventually led to intense competition. Companies like Compaq began producing IBM-compatible PCs, often at lower prices.
- Rise of the PC Clones: The open architecture of the IBM PC led to the rise of "PC clones," which eroded IBM's market share.
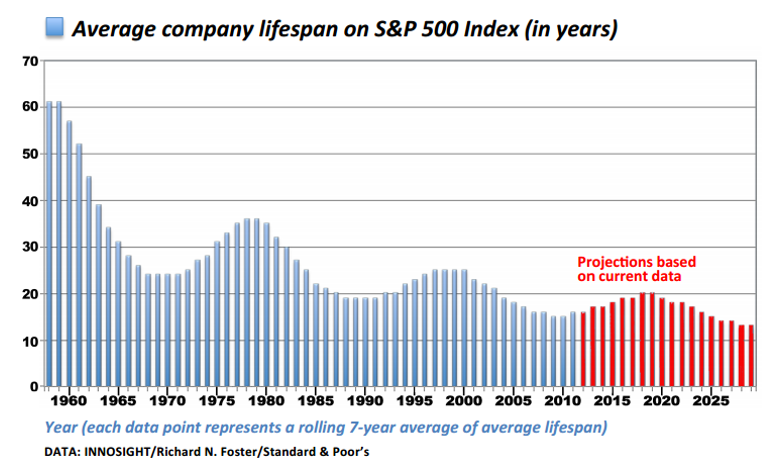







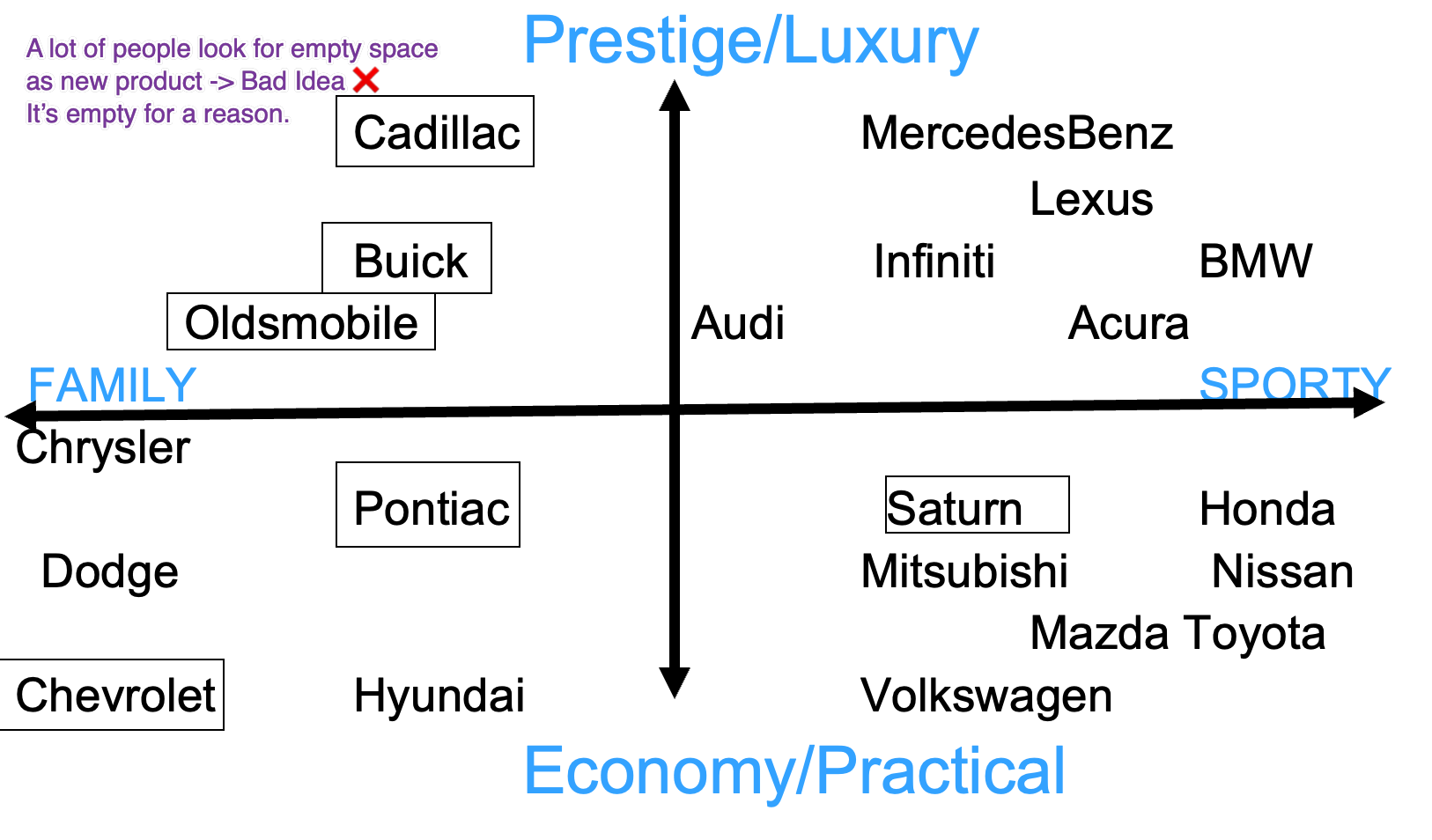 If you are looking to start a new car company where would you place in perception map?
If you are looking to start a new car company where would you place in perception map?